Generalized Anxiety Disorder & Substance Abuse in a Dual Diagnosis
People with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) are at increased risk for substance abuse, a trend supported by research that highlights the complex relationship between anxiety disorders and substance use.
Decoding Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A DSM-5 Guideline Overview
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), as defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), is a chronic and pervasive condition characterized by excessive worry and anxiety about various events or activities.
Unlike the focused anxiety seen in other anxiety disorders, GAD’s worry is broad, persistent, and often seems disproportionate to the actual likelihood or impact of the feared event. The DSM-5 provides specific criteria for the diagnosis of GAD, emphasizing the breadth and nature of the worry, its impact on functioning, and its differentiation from other anxiety disorders.

Diagnostic Criteria for GAD
Excessive Anxiety and Worry: Individuals with GAD experience excessive anxiety and worry about a variety of topics, events, or activities for most days over at least six months. This worry is difficult to control.
Number of Symptoms: The anxiety and worry are associated with three (or more) of the following six symptoms (with at least some symptoms present for more days than not for the past six months). Note that for children, only one symptom is required:
- Restlessness or feeling keyed up or on edge.
- Being easily fatigued.
- Difficulty concentrating or mind going blank.
- Irritability.
- Muscle tension.
- Sleep disturbance (difficulty falling or staying asleep, or restless, unsatisfying sleep).
Clinically Significant Distress or Impairment: The anxiety, worry, or physical symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
Distinction from Other Mental Disorders: The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition (e.g., hyperthyroidism) and does not better explain by another mental disorder (e.g., anxiety or worry about having panic attacks in Panic Disorder, negative evaluation in Social Anxiety Disorder, contamination or other obsessions in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, separation from attachment figures in Separation Anxiety Disorder, reminders of traumatic events in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, gaining weight in Anorexia Nervosa, physical complaints in Somatic Symptom Disorder, perceived appearance flaws in Body Dysmorphic Disorder, having a serious illness in Illness Anxiety Disorder, or the content of delusional beliefs in Schizophrenia or Delusional Disorder).
Features & Symtpoms
GAD is marked by a pervasive sense of worry that can interfere with daily activities. This worry is often about everyday matters, such as job responsibilities, health, finances, or minor matters such as chores, car repairs, or appointments.
The intensity, duration, or frequency of the worry is out of proportion to the actual likelihood or impact of the anticipated event. Individuals with GAD find it difficult to keep worrisome thoughts from interfering with their attention to tasks at hand and often have difficulty making decisions and handling uncertainty due to fears of making wrong choices.
Treatment for GAD
Effective treatment for GAD typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and medication. CBT helps individuals understand the relationship between their thoughts, behaviors, and symptoms, and develop strategies to change thinking patterns and manage anxiety. Medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are commonly used to help reduce the symptoms of GAD.
Understanding GAD through the DSM-5 framework is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, enabling individuals to manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Visual Guide: Symptom Spectrum of Anxiety Disorders
Understanding the nuanced symptoms of various anxiety disorders can be challenging. This illustrative graph, grounded in DSM-5 criteria, aims to simplify these differences. By comparing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) with Social Anxiety Disorder, Substance/Medication-Induced Anxiety Disorder, and Panic Disorder, we offer a clear visual breakdown of key symptoms unique to each disorder, facilitating easier comprehension.
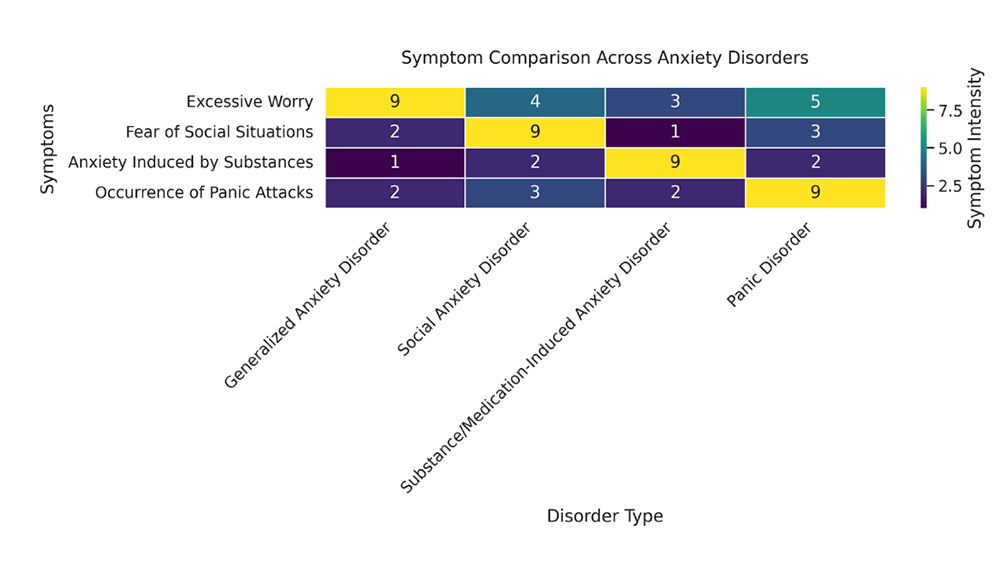
This graphical representation aims to provide a clear understanding of the unique symptom profiles associated with each anxiety disorder, facilitating better recognition and differentiation in clinical practice and personal understanding.
Recap on Identifying Types of Anxiety Disorders
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is marked by high levels of “Excessive Worry.”
Social Anxiety Disorder shows a significant “Fear of Social Situations.”
Substance/Medication-Induced Anxiety Disorder is characterized by “Anxiety Induced by Substances.”
Panic Disorder prominently features the “Occurrence of Panic Attacks.”
Disrupting Reality: The Truth About GAD
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) transcends common misconceptions. Far from just intense worry or a trait, it’s a serious condition impacting daily life, necessitating a debunking of myths through scientific insight.

Myth 1: GAD is just about being too worried
- The Truth: Recognized by the DSM-5, GAD involves persistent, excessive worry impacting daily life, not just normal stress.

Myth 2: Willpower Alone can Conquer GAD
The Truth: GAD’s complexity means treatment often includes CBT and possibly medication, as willpower isn’t enough.

Myth 3: GAD is not a real illness but a personality trait
The Truth: Research shows GAD is a legitimate disorder with changes in brain function and genetic links, not just a quirk.
Dual Challenges: Managing GAD and Substance Dependence Together
People with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) are at increased risk for substance abuse, a trend supported by research that highlights the complex relationship between anxiety disorders and substance use. Several factors contribute to this vulnerability.
It’s important for treatment plans for individuals with GAD to consider the potential for substance abuse. Integrated treatment approaches that address both GAD and substance use issues concurrently are often most effective. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication management, and support groups are integral components of a comprehensive treatment strategy.
Self-Medication
Individuals with GAD may turn to substances like alcohol or drugs as a way to self-medicate and alleviate their symptoms of anxiety. This attempt to manage or reduce the distressing symptoms of GAD can lead to dependency and addiction.
Increased Sensitivity to Stress
Research indicates that individuals with anxiety disorders, including GAD, have an increased sensitivity to stress. This heightened stress response may make substance use more appealing as a quick but temporary relief mechanism.
Treatment Challenges
The presence of both GAD and substance abuse complicates treatment and recovery. Substance use can exacerbate anxiety symptoms, making them more difficult to manage. Conversely, untreated anxiety can increase the risk of relapse in individuals recovering from substance abuse.
Research Data
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry suggests that nearly 20% of individuals with GAD also meet the criteria for a substance use disorder. This co-occurrence is particularly notable with alcohol and cannabis, which are among the most commonly abused substances by those trying to cope with anxiety symptoms.
Sources:
- National Institute on Mental Health (NIMH)
- The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry
These insights underscore the need for awareness, early intervention, and integrated treatment strategies to address the intertwined issues of GAD and substance abuse.
Navigating the Risks: Benzodiazepines in GAD Treatment
Prescribed medications like benzodiazepines are commonly used for their rapid relief of anxiety symptoms in Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), but their use complicates treatment due to the potential for addiction and dependence. Here are specific addictive benzodiazepines by brand and generic name, along with the risks they pose.
Risks Associated with Benzodiazepines in GAD Treatment:
- Alprazolam (Xanax): High potential for addiction and dependence; withdrawal can include severe anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and cognitive impairment.
- Clonazepam (Klonopin): Risk of long-term dependence; withdrawal symptoms can be severe, including panic attacks, tremors, and increased anxiety.
- Diazepam (Valium): Can lead to tolerance, requiring higher doses for the same effect; withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, agitation, and potential seizures.
- Lorazepam (Ativan): Dependence can develop even with short-term use; withdrawal can manifest as rebound anxiety, insomnia, and irritability.
Complications in GAD Treatment
Dependency and Withdrawal: The body can quickly become dependent on benzodiazepines, leading to a cycle of increased use and withdrawal symptoms when attempting to reduce or stop medication.
Rebound Anxiety: Upon discontinuation, patients may experience a resurgence of anxiety symptoms, often more intense than before starting medication, complicating the management of GAD.
Cognitive Impairment: Long-term use can impact cognitive functions, including memory and concentration, which may hinder daily functioning and the overall treatment process for GAD.
Treatment Resistance: Overreliance on benzodiazepines can make other treatment modalities, such as psychotherapy, less effective or more challenging to implement due to decreased patient engagement or reliance on medication as the primary form of relief.
Risk of Substance Use Disorder: The addictive nature of benzodiazepines raises the risk of developing a substance use disorder, further complicating treatment and recovery for individuals with GAD.
Given these risks, it’s crucial for healthcare providers to consider alternative, non-addictive treatments for GAD, such as SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors), SNRIs (Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors), and psychotherapeutic interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). These alternatives offer effective anxiety relief without the same potential for dependence and can be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both immediate symptoms and long-term management of GAD.
Transforming Anxiety: Essential Reads on General Anxiety Disorder
Explore the depths of Generalized Anxiety Disorder through these expert-authored books, offering insights and practical strategies for managing GAD. Authored by acclaimed clinicians, these books delve into effective treatment methodologies for GAD, equipping readers with knowledge and practices to navigate the complexities of anxiety and foster lasting relief and personal growth.
"The Generalized Anxiety Disorder Workbook: A Comprehensive CBT Guide for Coping with Uncertainty, Worry, and Fear"
by Melisa Robichaud, PhD, and Michel J. Dugas, PhD.
This workbook provides a step-by-step guide to conquering GAD through cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), focusing on overcoming excessive worry and embracing uncertainty.
"Mastery of Your Anxiety and Worry (MAW): Workbook"
by Richard E. Zinbarg, PhD, Michelle G. Craske, PhD, and David H. Barlow, PhD.
A resource developed by leading anxiety researchers, offering evidence-based techniques to reduce worry and anxiety, enhancing coping mechanisms through practical exercises.
"Overcoming Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Therapist Protocol"
by John R. White, PhD, and Arthur Freeman, EdD.
Aimed at therapists but invaluable for patients, this book outlines a structured approach to treating GAD, incorporating cognitive strategies and behavior modification techniques.
Reflections On Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Final Words for Families Considering Long-Term Treatment
The DSM-5’s comprehensive overview on Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) underscores the importance of accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies. Although benzodiazepines may provide immediate relief for GAD symptoms, their potential for addiction necessitates careful consideration and encourages the integration of safer alternatives like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and SSRIs.
Emphasizing these non-addictive treatments ensures a holistic approach, significantly enhancing the quality of life and long-term well-being for individuals grappling with GAD.

